The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) is an Enterprise Architecture framework that provides an approach for the design, planning, implementation, and governance of an enterprise information architecture. The architecture is modeled in four levels or dimensions: Business, Applications, Data and Technology. Each level is defined with a current state and a future state.
TOGAF has its own definition of what an architecture is, which in summary is “a formal description of a system, or a detailed plan of the system at the level of its components that guides its implementation”, or “the structure of components, their interrelationships, and the principles and guidelines that govern its design and evolution over time.”
An architecture framework is a set of tools that can be used to develop a wide spectrum of different architectures. This scheme must:
- Describe a methodology for defining an information system in terms of a set of building blocks that fit together properly.
- Contain a set of tools
- Provide a common vocabulary
- Include a list of recommended standards
- Include a list of products that are suitable for implementation of the building blocks
TOGAF meets these requirements.
TOGAF is based on four dimensions:
- Business Architecture (or Business Processes): which defines the business strategy, governance, structure, and key processes of the organization.
- Application Architecture: which provides a blueprint for each of the applications, the interactions between them and their relationships with the organization’s business processes.
- Data Architecture: which describes the structure of the logical and physical data of the organization, together with the structures and resources for managing these data.
- Technological Architecture: which describes the hardware, software and network structure required to support the implementation of the organization’s core applications.
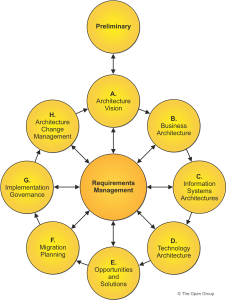
Architecture Development Method

